Mi chiamo Alessio Ippolito, sono nato il 9 agosto 1984 nella ridente cittadina di Frascati (Roma), situata nel cuore nevralgico dei castelli romani. Sono un imprenditore digitale attivo dal 2008, autore e giornalista finanziario dal 2022 iscritto presso l’OdG del Lazio[1].
Ho iniziato a muovere i primissimi passi nel mondo digitale nel biennio 2007/2008, anno in cui ho lanciato il mio primo sito web, realizzato completamente da zero: era un semplicissimo blog di natura economica, all’interno del quale pubblicavo approfondimenti e pillole finanziarie frutto dei miei appunti presi durante le mie lezioni di micro e macroeconomia all’Università la Sapienza di Roma, indirizzo di studio Economia e finanza per la Gestione d’Impresa: un importante percorso di studi che mi ha permesso di apprendere le mie prime skill imprenditoriali.
Oggi sono considerato tra le principali eccellenze imprenditoriali dell’editoria italiana nel settore delle criptovalute, trading e finanza personale, dove ricopro un ruolo di spicco grazie all’autorevolezza dei miei brand online.
About me
Ecco un breve riassunto di chi sono e di cosa mi occupo ogni giorno con passione e dedizione nel mondo digitale e dell’informazione:
- Sono un Imprenditore Digitale – Fondatore e amministratore unico di Alessio Ippolito S.R.L., casa editrice digitale nata nel 2017, specializzata nella produzione di contenuti di alta qualità nel settore finanziario, crypto, e Web3.
- Ho fondato Criptovaluta.it® – È la testata giornalistica indipendente n.1 in Italia sul mondo di Bitcoin e delle criptovalute, online dal 2017. Oggi è una delle più autorevoli anche a livello internazionale, con menzioni e riconoscimenti ottenuti sulle più autorevoli testate giornalistiche mondiali come The Block, BeInCrypto, Decrypt e tante altre. Vedi la pagina ufficiale press/media di Criptovaluta.it.
- Sono un Giornalista – Iscritto all’Ordine dei Giornalisti, ho partecipato a 4 puntate di prima serata di “Chi l’ha visto?” come esperto sul tema delle truffe online e finanziarie, a tutela dei risparmiatori. Se ne è parlato anche su le più autorevoli testate nazionali come IlGiornale.it.
- Sono autore Bestseller su Amazon e Google Books di libri tematici sul trading online, impresa & business, Bitcoin e crypto. Il mio libro “Trading Online, Bitcoin e Crypto: Analisi Tecnica, Segnali e Strategie | Da ZERO a Trader PRO” è tra i più venduti tra i consigliati di Amazon.
- Autore Investing.com – Da febbraio 2022 sono autore della più popolare rivista finanziaria del mondo, Investing.com – qui potete leggere i miei pezzi firmati per Investing.com Italia.
- Sono SEO e web marketer – Dal 2008 mi occupo della realizzazione, partendo da zero, di pagine blog, siti web e portali di informazione ottimizzandoli per i motori di ricerca attraverso la SEO – non ho mai fatto SEO con portafogli di terzi: tutta la SEO fatta nella mia vita è stata meramente rivolta ai miei progetti personali e da me finanziati.
- Autore del substack newsletter “Alessio Ippolito” che conta oltre 3.250 iscritti.
- Popular Investor eToro: dal 25 agosto 2025, dopo anni di lavoro come trader privato, sono diventato ufficialmente Popular Investor Champion in eToro, uno dei pochi in Italia ad aver raggiunto questo traguardo in soli 2 mesi (Status Champion ricevuto inizio novembre 2025).
- Affiliate marketer – sono nel campo delle affiliazioni sul trading, prodotti finanziari e in passato anche nutra, dal 2012. Ho finanziato tutti i miei principali progetti potendo far leva sulla mia esperienza sull’utilizzo delle tecniche di affiliation marketing.
- Mi occupo di sviluppo e innovazione – Ogni progetto editoriale che seguo è pensato per crescere, internazionalizzarsi e scalare con strategie digitali. Monitoro i trend USA e Giappone per identificare nuove opportunità imprenditoriali.
- Podcaster – Progetto e gestisco il popolare Podcast su Spotify di Criptovaluta.it
- Telegram expert – Ho fondato il canale Telegram di Criptovaluta.it®, che conta oggi oltre 43.000 iscritti e con oltre 2.8 milioni di commenti gestiti al mese è oggi il primo canale tematico sul mondo delle crypto con più interazioni in Italia.
- Sono un publisher, nato come autodidatta nel lontano 2007/ 2008 – Dopo diversi studi le mie prime attività digitali risalgono al 2008. Da allora ho fondato e gestito diversi progetti editoriali realizzandoli completamente da zero e portandoli sino al successo.
- Nozioni di programmazione – Conosco i linguaggi di programmazione HTML, CSS e Javascript ed ho conoscenze base di React.
- Team leader di ricerca e sviluppo – Sono figura principale e team leader per la ricerca e sviluppo su diversi dei marchi di proprietà della ALESSIO IPPOLITO S.R.L. Editore. Grazie alle mie indicazioni e progettazioni fornite agli sviluppatori (interni o figure esterne assunte a prestazioni dalla mia azienda, ndr) vengono sviluppati componenti interattivi ad alto valore aggiunto applicazioni web o mobile, plugin, gestionali e/o altri elementi grafici o tecnici.
- Innovazione e sviluppo nel mondo del trading in Italia – Sono stato il primo a portare sui miei siti componenti interattivi che diano la possibilità alla community di votare le migliori piattaforme trading in modo imparziale e libero, trasparente e univoco.
- Gestione economica, patrimoniale e contabile aziendale – Sono l’unica figura societaria che si preoccupa di gestire il patrimonio societario, gestire la contabilità di cassa, occuparsi dei rapporti con i fornitori, fornire rendicontazioni agli studi commercialisti, gestione di fatture attive e passive, programmare investimenti di breve, medio o lungo periodo. Al sottoscritto fanno capo tutte le scelte strategico-societarie atte alla conservazione e sviluppo del proprio business-model, adattandolo alle repentine evoluzioni del settore.
- Intelligenza artificiale – Dal 2023 studio da vicino l’intelligenza artificiale e le sue applicazioni per l’ottimizzazione e pianificazione dei processi aziendali.
- Gestisco altri progetti editoriali – Oltre a Criptovaluta.it, sono anche fondatore e responsabile di:
- tradingonline.com – portale educativo e divulgativo per chi vuole imparare a investire online
- guidatradingonline.net – acquistato nel 2019 (fonte ANSA)
- investireinborsa.org – storico sito su Google ultra verticale focalizzato sugli investimenti in borsa e finanza personale – è attivo dal 2007
- giocareinborsa.net – autorevole portale specializzato sulla classificazione delle migliori azioni di ogni comparto, analisi e recensioni delle piattaforme di investimento e online dal 2009
- Sono un Content Creator e Divulgatore Digitale – Mi occupo della creazione, promozione e strategia dei contenuti per tutti i brand editoriali del gruppo. Scrivo regolarmente su Quora (profilo Quora), Medium (profilo Medium) e Reddit (profilo Reddit) dove condivido riflessioni su business, Web3, innovazione e marketing.
- Gestisco canali YouTube di successo nel settore intrattenimento e animazione per bambini – Minecraft animations, 2 popolari canali da oltre 6 milioni di iscritti complessivi e oltre 1 miliardo di visualizzazioni complessive ottenute in soli 24 mesi (dati rilevati al 19 maggio 2025).
- Ambedue questi progetti sono stati ideati, sviluppati e scalati da me partendo da zero, portando contenuti in stile Minecraft a un pubblico globale di bambini.
- Ad agosto 25 ne ho avviato un terzo, più incentrato sui long form (video lunghi) e per ora conta poche centinaia di iscrizioni.
- Sono un Digital PR expert e Brand Strategist – Collaboro con grandi brand internazionali del mondo crypto e finanziario, coordinando campagne di visibilità e partnership commerciali altamente performanti, ottimizzandone i risultati al fine di soddisfare le esigenze dei partner multinazionali.
- Sono un Blogger, Video editor basic e Social Media Manager – Scrivo regolarmente articoli su tematiche economiche, Web3, NFT, blockchain, e marketing digitale. Gestisco profili social aziendali con migliaia di follower attivi e campagne ad alto impatto. Mi diletto inoltre a condividere qualche risata, pensiero e riflessione sul mio account personale su TikTok.
Leggi di più sulla biografia di Alessio Ippolito.
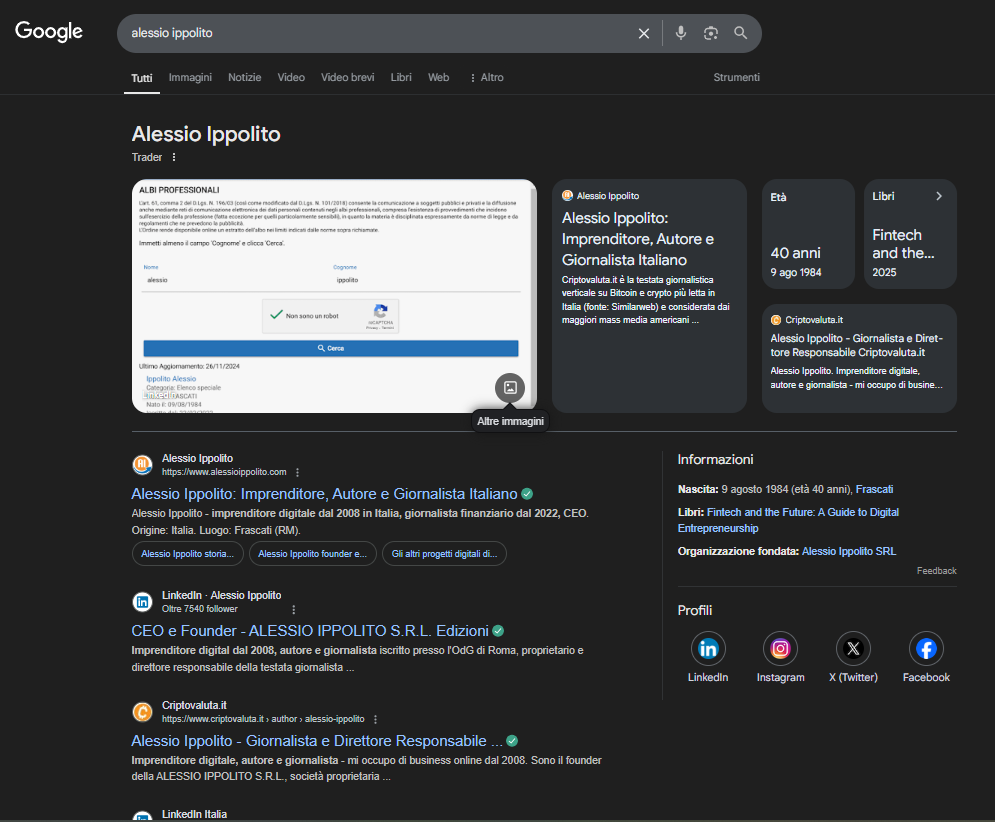
Alessio Ippolito su Google
La mia figura professionale è inquadrata in modo chiaro e trasparente su Google e a questo indirizzo puoi prenderne visione: Ricerca Alessio Ippolito su Google.it
Alessio Ippolito newsletter – Substack
Sono autore del Substack newsletter che prende il mio nome: ogni lunedì alle 17:17 condivido con i miei oltre 3.200 readers un contenuto di approfondimento che spazia dal mondo crypto al business, senza compromessi e peli sulla lingua.
L’iscrizione è gratuita e puoi farla da qui:
Alessio Ippolito storia professionale, carriera e il successo
Cerco di riassumere alcuni dei fatti più salienti, cercando di essere estremamente sintetico. Dopo diversi anni di studio/lavoro come libero professionista intrapresi tra il 2008 e il 2011, nel 2012 ho fondato la mia primissima azienda, era una semplice ditta individuale il cui nome: “Ditta Individuale di Alessio Ippolito” (ho sempre avuto tanta inventiva nella scelta dei nomi delle mie aziende eh), che due anni più tardi l’ho trasformata in una Società in Accomandita Semplice (ALESSIO IPPOLITO S.A.S.).
Considerata la crescita anche della SAS, nel 2017 – insieme al mio studio commercialista – abbiamo deciso di fare un ennesimo passo in avanti, realizzando uno dei miei sogni: creare una società di capitali a mio nome e totalmente da me gestita, quella che è ad oggi la mia più grande soddisfazione e motivo di orgoglio, la Alessio Ippolito S.R.L. Editore. Questa società è proprietaria di un network di 6 siti web principali, tra cui le note pubblicazioni online come Criptovaluta.it® e TradingOnline.com®.
Il 2017 è stato un anno particolarmente “fortunato” per il prosieguo della mia carriera imprenditoriale: fu l’anno nel quale acquistai il dominio Criptovaluta.it, il cui sviluppo fu completato pochi mesi più tardi. Nel 2018 il sito andò definitivamente online, con un’ambizione ben definitiva: diventare il punto di riferimento in Italia nel panorama crypto.
Guarda qui il network della Alessio Ippolito.
Alessio Ippolito founder e unico proprietario di Criptovaluta.it®
Criptovaluta.it è nata come blog, dopo pochi mesi è entrata a far parte delle fonti di notizie in Google News. Dopo due soli anni di “gavetta“, nel 2020 decisi di dare una spinta al sito, focalizzando su di esso tutti i miei sforzi economici, imprenditoriali, di ricerca e sviluppo. Il primo grande boom di traffico arrivò nel 2021. Nel corso degli anni si è imposto come crypto news media outlet leader italiano, consolidando la sua posizione di leadership, misurabile sia in termini di autorevolezza ed influenza mediatica nel settore, sia utilizzando diversi parametri di analisi delle performance come Similarweb, Google Search console e Google Analitycs.
Risorse utili:
Criptovaluta.it®- crypto news media outlet leader in Italia
Criptovaluta.it è la testata giornalistica verticale su Bitcoin e crypto più letta in Italia (fonte: Similarweb) e considerata dai maggiori mass media americani di settore come Decrypt, Beincrypto e TheBlock, che sono i notiziari di settore più autorevoli e famosi al mondo.
Riprendiamo quanto si legge sul sito ufficiale in relazione alla consacrazione di Criptovaluta.it nel panorama della crypto-informazione in Italia – anno 2021:
Il boom di Criptovaluta.it nel 2021 è stato evidente. Siamo il sito sulle criptovalute più seguito in Italia.
Marzo 2021: Sessioni del mese 542.000
Aprile 2021: Circa 1.000.000 di sessioni, quindi il doppio rispetto al mese precedente.
Totale 1° QUADRIMESTRE: 2.000.000 sessioni circa
Confronto 1° QUADRIMESTRE 2021 con 1° QUADRIMESTRE 2020: 2.000.0000 sessioni circa VS 72.200 per una crescita complessiva di sessioni pari a 2.451,51%.
Nel maggio del 2021 Criptovaluta.it raggiunge il suo record storico di visite: 1.400.000+ accessi in un mese, diventando così il primo sito tematico sulle criptovalute più letto in Italia. Tradotto in termini percentuali, la crescita del sito è stata di +50% rispetto al mese di Aprile 2021, e addirittura del 8.157,34% rispetto ad un anno fa (Maggio 2020).
Secondo semestre 2021: 9 milioni di accessi complessivi. In termini di percentuali, significa una crescita dell’8.400% rispetto al semestre del 2020.
Criptovaluta.it® diventa marchio registrato
Il 15 dicembre 2021 la ALESSIO IPPOLITO S.R.L. ha depositato il marchio presso il MiSE (Ministero per lo Sviluppo Economico) per proteggerne integralmente tutte le sue attività, il suo business, difendendone i diritti d’autore. La registrazione effettiva del marchio è avvenuta il 5 settembre 2022[5].

Criptovaluta.it® diventa testata giornalistica
Sulle ali dell’entusiasmo, al fine di dare ancora una maggiore credibilità a quello che in realtà era ancora un semplice blog amatoriale, intrapresi dai primissimi giorni del 2022 una lunga ed estenuante rincorsa alla registrazione del blog a Testata Giornalistica iscritta presso un autorevole Tribunale italiano. Ci provai 3 volte: Tivoli, Roma e poi Milano e, dopo mesi e mesi di snervanti pratiche burocratiche, carte su carte e salate parcelle pagate ai rispettivi professionisti, precisamente il 10 ottobre 2022, finalmente Criptovaluta.it® diventa ufficialmente una testata giornalistica iscritta presso il Tribunale di Milano col numero 12776/2022 – Num. Reg. Stampa: 143[6] – esattamente un mese e mezzo dopo la registrazione del marchio.
Il successo di Criptovaluta.it®
Con una media su anno di oltre 2.000.000 unici mensili e 3.500.000 milioni di pagine viste al mese, mezzo milione di followers attivi sui social e circa 2.7 milioni di commenti al mese presenti sulla nostra community Telegram, Criptovaluta.it è riconosciuta dall’unanimità degli addetti ai lavori del mercato crypto in Italia, come il media leader del settore, sia in termini di qualità dei contenuti, tempismo nella pubblicazione delle notizie, esclusività ed espressione dei concetti anche più complessi.
Le principali testate giornalistiche americane come TheBlock e Decrypt, parlando della testata da me diretta, la definiscono come “most important crypto news media outlet in Italy“. Riprese giornalistiche, contatti istituzionali (vedasi ns esclusive con i protagonisti del Parlamento Italiano), interviste TV, menzioni delle più autorevoli testate nazionali, citazioni televisive, confermano l’autorevolezza di questo marchio. Puoi approfondire questo argomento dando uno sguardo alla pagina parlano di me.
Alessio Ippolito libri
Su Google Books puoi prendere visione e scaricare le mie pubblicazioni. I miei libri sono rivolti a tutti coloro che sono interessati al mondo dell’imprenditoria, del giornalismo e del futuro digitale con un occhio di riguardo al trading online, alle criptovalute con tutte le loro implicazioni.
Le mie pubblicazioni su Amazon Books e Google Play Libri
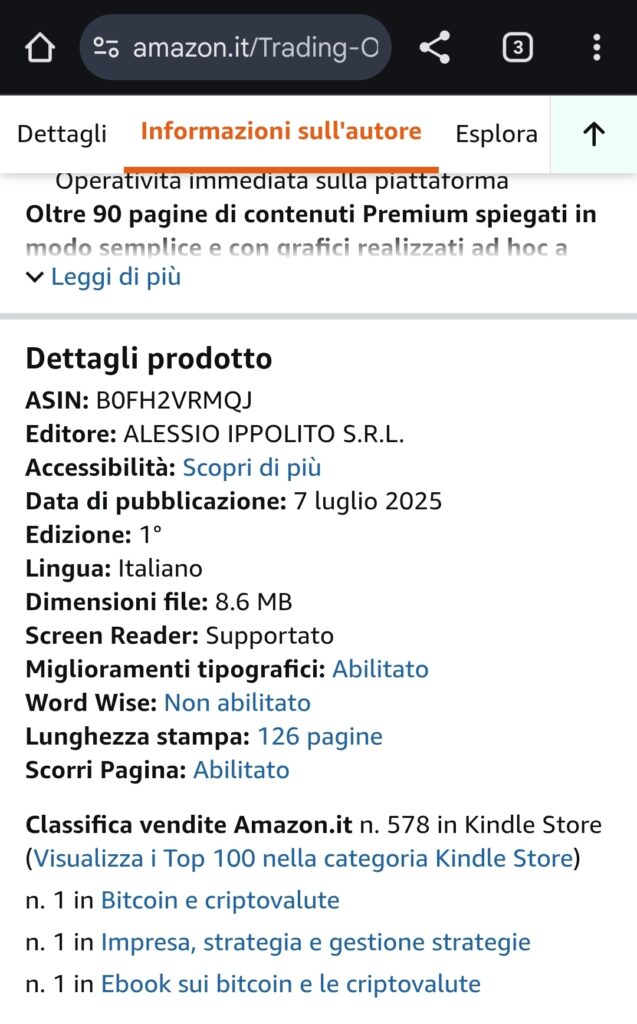
>>> Guardalo su Amazon <<<
Titolo: Trading Online, Bitcoin e Crypto: Analisi Tecnica, Segnali e Strategie | Da ZERO a Trader PRO
Anno: 2025
Formato: Kindle eBook
Amazon Store: Visita la mia pagina autore su Amazon
Vuoi invece comprarlo su Google Books? Visita questo link.
Alessio Ippolito – Autore Bestseller su Amazon
Con il libro “Trading Online, Bitcoin e Crypto: Analisi Tecnica, Segnali e Strategie | Da ZERO a Trader PRO” sono diventato autore bestseller su Amazon e sono finito tra i consigliati dal leader dello shopping online.


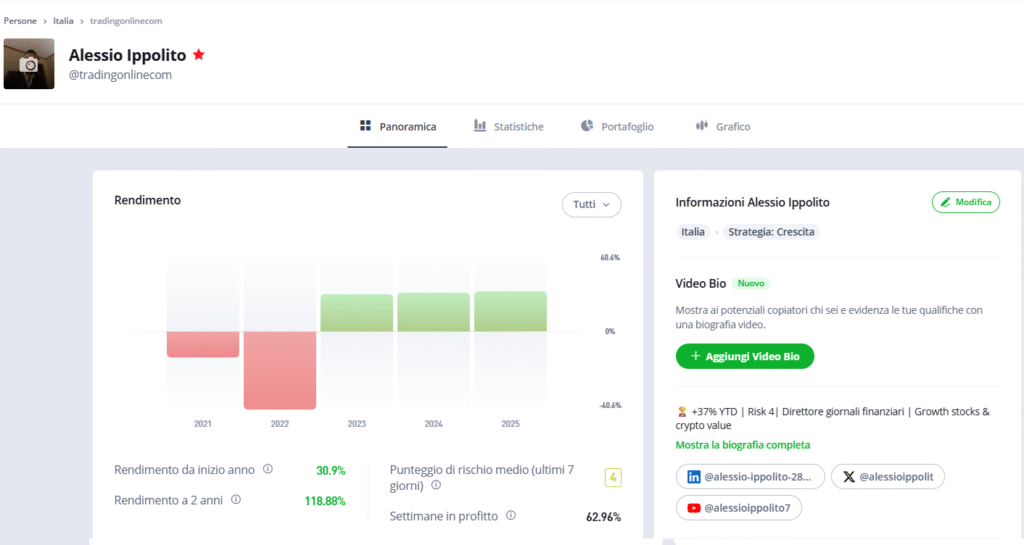
Alessio Ippolito Popular Investor Champion su eToro
Dal 25 agosto 2025 sono stato finalmente eletto Popular Investor in eToro ed insignito al pregiato status di Popular Investor Champion stellina rossa soltanto due mesi dopo (tra i pochissimi in Italia ad aver raggiunto questo traguardo solo dopo due mesi, ndr),
Un ennesimo passo importante per me anche come piccolo investitore privato che, oltre a fare l’imprenditore a tempo pieno dal 2008, conserva da sempre in se la passione per il trading.
E così, dopo anni di lavoro come trader su Etoro, mi hanno insignito di questo importante riconoscimento e mi auguro di poter condividere le mie analisi e decisioni strategiche insieme a quanti più lettori e amici followers nel corso del tempo.
Analisi che approfondirò soprattutto anche all’interno della mia newsletter settimanale all’indirizzo alessioippolito.it.
A questo indirizzo puoi vedere il mio profilo e registrarti per iniziare a seguirmi.
Gli altri progetti digitali di successo da me realizzati partendo da zero
Oltre ad essere il direttore responsabile di Criptovaluta.it, sono anche il direttore di altri marchi prestigiosi, primo fra tutti TradingOnline.com®, il principale quotidiano finanziario sul trading online in Italia. Sono poi anche direttore di un sito web di nicchia e storico sul trading online in Italia chiamato GuidaTradingOnline.net, e gestisco siti estremamente verticali dedicati agli investimenti in borsa online come Investireinborsa.org e Giocareinborsa.net.
Infine, a novembre 2024, ho lanciato anche un sito news sviluppato su un dominio storico .it LLL (3 lettere, ormai introvabile tipologia di domini, ndr) e si chiama Gex.it: questo sito si occupa di pubblicare ogni giorno le ultimissime notizie dal mondo delle nuove tecnologie, l’intelligenza artificiale, il deep tech e la Web3.
Qui puoi consultare il network della ALESSIO IPPOLITO S.R.L. editore.
Il mio impiego professionale sui principali portali informativi del network

Direttore di Criptovaluta.it®: Dal 2017, anno della sua nascita, sono il direttore responsabile a tempo pieno di Criptovaluta.it, la più seguita testata giornalistica italiana verticale su Bitcoin e crypto, di respiro internazionale, con riconoscimenti e menzioni TV, radiofoniche e dal mainstream internazionale. Testate crypto USA blasonate come TheBlock o Decrypt ci definiscono come il principale “crypto news media outlet italiano”. Con oltre 30 milioni di lettori negli ultimi due anni e una community tra le più influenti del settore.
Ogni settimana su Criptovaluta.it vengono pubblicate +100 articoli tra news, analisi, esclusive, interviste e approfondimenti legati al mondo crypto, osservando particolare attenzione ai principali focus del momento. Può vantare di menzioni e riconoscimenti internazionali, interviste ai tutti i più grandi personaggi influenti del settore, citazioni ed apparizioni radiofoniche e televisive. Criptovaluta.it è un marchio registrato di proprietà della Alessio Ippolito S.R.L.

Direttore di Guidatradingonline.net: Dall’ottobre del 2016 a giugno del 2020 sono stato collaboratore esterno a tempo pieno per lo sviluppo di www.guidatradingonline.net, chiamato dal fondatore Antonio Loverato – per il quale ho curato, insieme al lui, il lancio e tutta la fase di creazione della struttura contenutistico. Guidatradingonline.net è un sito verticale esclusivamente dedicato a 360° sul mondo del #tradingonline. Offre guide complete dedicate allo studio e alla formazione di principianti che vogliono scoprire o approfondire il mondo degli investimenti finanziari.
Ad aprile 2019 la ALESSIO IPPOLITO S.R.L. ha acquisito il portale e sono diventato il direttore generale a tempo pieno.
Dal 30 gennaio 2025 ho assunto un ruolo manageriale completo su Guidatradingonline.net per sviluppare ulteriormente il suo brand dopo aver ottimizzato tutta la parte front-end del sito, iniziata verso fine 2023. Questo giornale è stato considerato per anni il punto di riferimento sulla ricerca organica di Google.it per tutti coloro che vogliono iniziare a muovere i primissimi passi con il trading online partendo da zero.
Per la ALESSIO IPPOLITO S.R.L. Guidatradingonline.net rappresenta da anni un caposaldo del suo network SEO verticale sul trading.
La società conversa ottime aspettative di crescita di questa testata di approfondimento e il mio ruolo sarà proprio quello di riuscire ad ottenere gli obiettivi prefissati in sede decisionale, con strategie operative e di marketing appositamente studiate.

Direttore di Investireinborsa.org: Sono direttore generale a tempo pieno da febbraio 2024, mentre da dicembre 2024 ricopro su Investireinborsa.org anche la posizione di brand developer, con l’obiettivo di migliorare visibilità, posizionamento strategico e percezione del brand Investireinborsa.org online.

Direttore di Giocareinborsa.net: Da giugno 2024 la ALESSIO IPPOLITO SRL ha assorbito il brand Giocareinborsa.net a giugno 2024. Per questo sito mi occupo di gestire lo sviluppo strategico-editoriale nonchè migliorare la percezione del marchio sui motori di ricerca.

Direttore di TradingOnline.com®: Da dicembre 2020 sono proprietario e direttore responsabile di TradingOnline.com, il il sito ufficiale sul #tradingonline attualmente disponibile in italiano. News, guide ed approfondimenti relativi al trading, azioni, forex, crypto, obbligazioni e principali assets di borsa.
Direttore di GEX.it NEWS: Da novembre 2024, data di messa online del progetto, mi occupo dello sviluppo strategico del brand, del project management e di tutto ciò che riguarda la comunicazione, firmandone editorialmente tutte le principali notizie dedicate al mondo della tecnologia e della Web3. Gex.it è un prodotto della ALESSIO IPPOLITO S.R.L. Editore.
Puoi approfondire più nel dettaglio i miei ruoli assunti nel corso del tempo sui vari siti web, visitando il mio profilo Linkedin.
La mia iscrizione presso l’Ordine dei Giornalisti del Lazio
Sono giornalista iscritto all’Ordine dei Giornalisti del Lazio[6] dal 22 febbraio 2022 (Elenco Speciale – Giornalisti Tecnici Specializzati). L’iscrizione all’elenco speciale dei giornalisti è destinata ai professionisti che presentano domanda per conto di un editore di un quotidiano online per essere registrati come Testata giornalistica presso un tribunale (tali richieste sono soggette a verifica e potrebbero essere respinte).
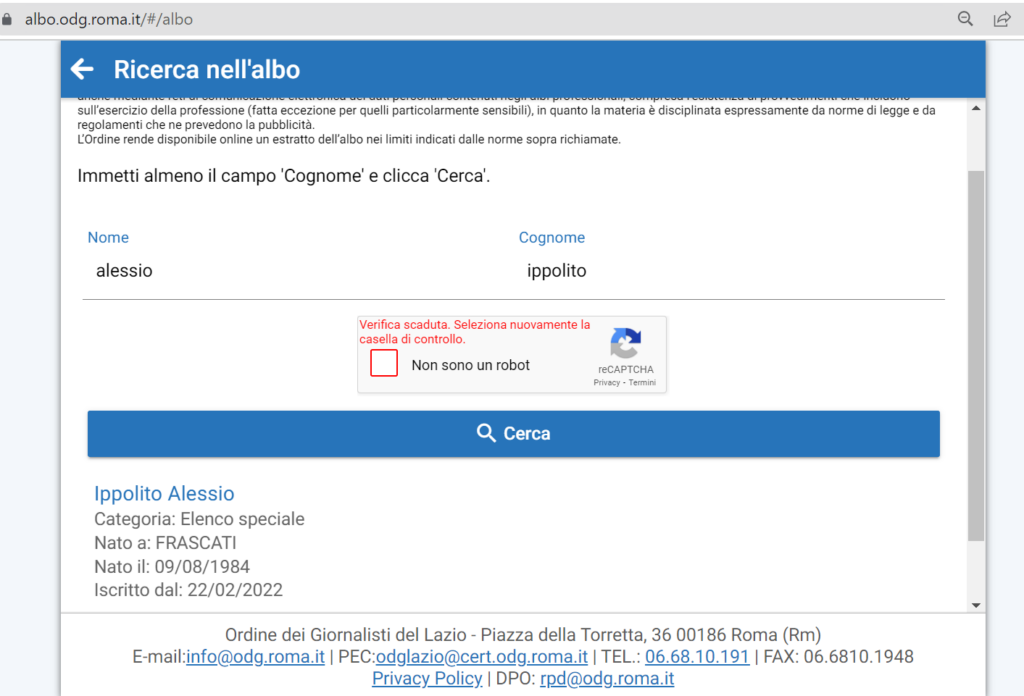
La credibilità acquisita dal giornale Criptovaluta.it nel 2021 ha spinto la mia azienda – proprietaria del sito – a registrare prima il marchio e, poco dopo, a presentare domanda al Tribunale di Milano per la registrazione come testata giornalistica.
Alessio Ippolito mindset e principi imprenditoriali
Sempre alla ricerca di innovazione, in particolare dal mondo del web e delle nuove tecnologie, sono costantemente interessato a esplorare nuove opportunità di investimento in startup e idee imprenditoriali.
Tutti i miei brand di maggiore successo sul web sono sempre partiti con la stessa logica operativa:
- Nasce l’idea;
- La studio ed approfondisco al fine di comprenderne la fattibilità;
- Inizio a raccogliere il materiale e tutte le risorse utili per studiare ed approfondire il progetto;
- Eseguo una prima analisi dei costi iniziali, quindi predispongo il budget;
- Pianifico il team di sviluppo;
- Metto in pratica l’idea, dandole forma e vita;
- La mia idea è diventata realtà.
Ma, cosa ancora più importante, è crederci dal primo istante, fissare il target e massimizzarne il focus: senza cuore e mente ogni iniziativa imprenditoriale diventa vana.
Quanto guadagna Alessio Ippolito?
Stando alle ricerche su Google, se lo chiedono in molti. Sono il founder della mia società – la ALESSIO IPPOLITO S.R.L. – quindi il mio guadagno dipende essenzialmente dalle performance, misurabili in termine di utile, ottenuti annualmente dalla mia azienda e potete prenderne visione leggendo il paragrafo: ALESSIO IPPOLITO S.R.L. fatturato
La mia gestione del tempo
Dio solo sa, permettetemi una battuta prima di concludere, quanto tempo ha a sua disposizione un imprenditore, specie se digitale 🙂 davvero tanto, a tal punto che… magari alle due di notte si trova a dover mandare un task all’assistenza perchè un suo sito è sotto attacco hacker, a fare preventivi argomentandoli con 3.000 parole (almeno) ad una multinazionale israeliana perchè loro “o ti sbrighi o da domani non ti prendono più in considerazione“, oppure il primo maggio deve correre davanti al PC perchè ti ha scritto una multinazionale finance chiedendoti di risolvere alcune “compliance rules” entro e non oltre 24H, pena il blocco dei conti di affiliazione e di conseguenza i pagamenti.
Ovviamente tutti fatti realmente accaduti...
Ad ogni modo, dopo 17 anni di attività, potrei scrivere interi libri su questa tematica, tuttavia non è nel mio interesse tediarvi cagion di questo: con gli anni impari infatti a gestire meglio il tuo tempo, ritagliandoti del tempo libero per vivere una vita con la V maiuscola. Con l’esperienza impari a capire come quando e cosa delegare ai tuoi stimati collaboratori e ad ottimizzare meglio il tuo tempo lavorativo.
La mia attività su Reddit
Sono molto attivo su Reddit in quanto lo ritengo un social di condivisione sano, equilibrato e davvero ricco di informazioni: il suo boom di traffico in tutto il mondo ottenuto negli ultimi due anni non mi coglie di sorpresa bensì conferma tutta la sua qualità. Perchè sta avendo così successo Reddit? Perchè pur essendo un social multi-argomento, è suddiviso per community (subreddit) dove le persone condividono informazioni, contenuti, propongono domande e postano idee.
Con uno sguardo più imprenditoriale e talvolta anche SEO, può rappresentare un ottimo luogo virtuale ove mettersi in mostra e mostrare a tante persone le proprie abilità professionali.
Potete seguirmi su Reddit qui: @supermindxy – Alessio Ippolito Reddit
La mia expertise su Quora
Sono attivo anche su Quora come esperto di criptovalute, trading e finanza digitale. Condivido regolarmente approfondimenti, analisi e consigli pratici basati sulla mia esperienza nel settore.
Le mie risposte hanno aiutato migliaia di persone a comprendere meglio il mondo delle criptovalute e a prendere decisioni di investimento più consapevoli.
Seguimi su Quora per accedere ai miei contenuti esclusivi e porre direttamente le tue domande sul mondo crypto e trading.
Alcune delle mie risposte più popolari:
- 🥇Conviene investire in Bitcoin? Davvero potrà arrivare fino a 200.000$ di valore?
- 🥈Conoscete corsi buoni per imparare ad investire in borsa?
- 🥉Quali sono le migliori azioni da comprare in questo periodo di crisi causa Covid-19)
Alessio Ippolito passioni, hobby sport e… tempo libero
Quando parlo del mio lavoro e rispondo a conoscenti e fan sempre molto interessati alla mia professione, a volte mi chiedono anche: “e nel tempo libero che fai?“.
Concedetemi una battuta: perchè davvero ne resta?
Nel corso degli anni ho sicuramente imparato a gestire meglio il mio tempo, per ritagliarmi del tempo tutto per me, per le mie attività personali extra lavoro e, ovviamente, per le mie passioni: questo mi permette di garantirmi un buon stile di vita. Le mie passioni più grandi sono sicuramente la palestra, mantenimento e cura del mio aspetto fisico, la passione per i viaggi (oltre a quelli di lavoro, ndr), seguire lo sport in genere e soprattutto il calcio… la sregolata passione per l’AS Roma… non me ne vogliano ora i tifosi delle squadre avversarie 🙂
Amo anche cucinare piatti fit, leggere libri specialmente rivolti alla crescita personale, alla finanza e alla gestione d’impresa e approfondire i temi delle nuove tecnologie applicate al web, come l’innovazione dell’intelligenza artificiale e tutte le sue implicazioni, approfondendo varie risorse come libri, risorse universitarie, studi e, perchè no, anche video su Youtube. Da aprile ho anche aperto un account su TikTok dove adoro parlare anche di altro, condividere le mie passioni, fotogrammi di vita privata e concederci anche qualche sana risata.
Alessio Ippolito Wikipedia
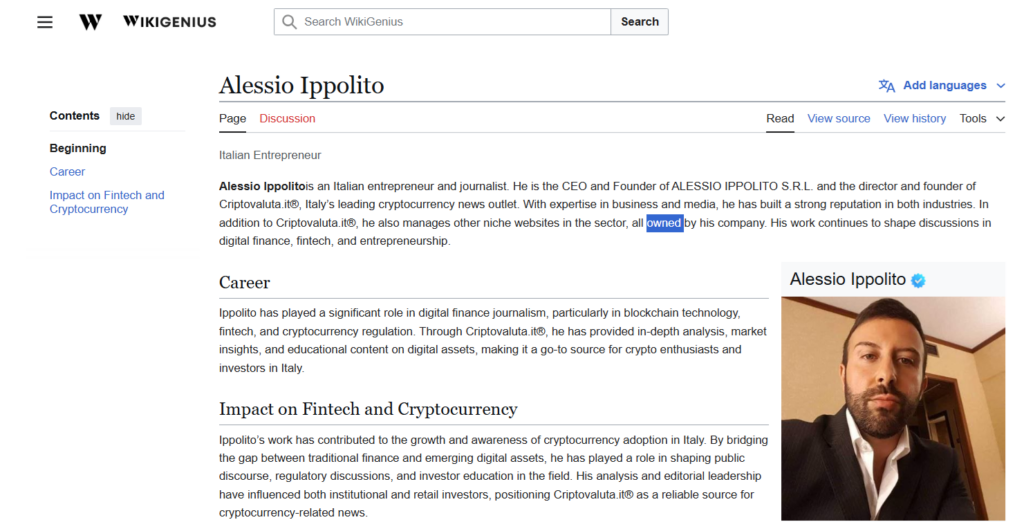
Sono stato menzionato da ms.Wikipedia.org, per via della mia autorevolezza verificabile nel mondo digital italiano, specialmodo interconnessa all’autorevolezza determinata da Criptovaluta.it.
Sono anche presente su Wikipedia in lingua inglese.
Wikipage
Intorno alla metà di febbraio 2025 ho avuto il piacere di scoprire che il noto portale wikigenius mi ha dedicato una pagina descrivendo la mia professione.
I miei articoli su Linkedin
Sul mio profilo personale LinkedIn, puoi trovare post e analisi approfondite sui settori chiave di mio interesse (trading online, Bitcoin e criptovalute), nonché approfondimenti e riflessioni su editoria e giornalismo.
È naturale aspettarsi che gran parte dei miei contenuti pubblicati su LinkedIn siano strettamente correlati ai miei argomenti di maggior interesse: #Bitcoin #Crypto #giornalismo #editoria #impresa ed #imprenditoria.
Profilo professionale Crunchbase – Imprenditore
La mia azienda – ALESSIO IPPOLITO S.R.L. – è regolarmente iscritta presso il sito Crunchbase, popolare sito internazionale dove milioni di professionisti condividono informazioni per accrescere il proprio business, puntando su risorse umane, ricerca, raccolta fondi e sviluppo.
E su Crunchbase, oltre alla mia azienda, sono anche registrato come professionista (imprenditore), con occupazione fissa presso quest’ultima.
Social Alessio Ippolito (Reddit, Instagram, X, TikTok, Linkedin)
Ecco l’elenco completo dei miei principali social, alcuni dei quali hanno un printing più personale (come Instagram e Tiktok) mentre altri sono più di stampo professionale come il sopracitato Quora, come Facebook, X e Linkedin, oppure ibrido come il già citato Reddit, dove condivido opinioni relative alle mie passioni nonché inerente le mie conoscenze professionali:
Per l’elenco completo di tutti i miei social network e portali dove sono registrato visita la pagina: elenco social network Alessio Ippolito
Alessio Ippolito ultimi video su TikTok
Alessio Ippolito vita privata
Cosa volete sapere nello specifico? Tengo molto alla mia privacy, anche se chi mi conosce di persona magari non lo direbbe (si, sono normalmente un grande chiacchierone, per alcuni versi quasi logorroico 🙂 ), ma potete vedere qualche storia anche relativa a questo magari seguendomi sul mio profilo Instagram, dove comunque condivido anche storie duranti i miei viaggi personali e lavorati ma anche i miei hobby e le mie passioni.
Disclaimer informativo: Tutte le informazioni ivi raccolte in questa pagina sono autentiche, comprovate e certificate.
[wikidata]